Fixed broadband services have seen increasing speeds in the last few years across the Middle East, with Gulf countries leading the way in delivering high speed connectivity along with a host of broadband-based services such as TV and gaming channels.
Disparity of fixed broadband development in the region
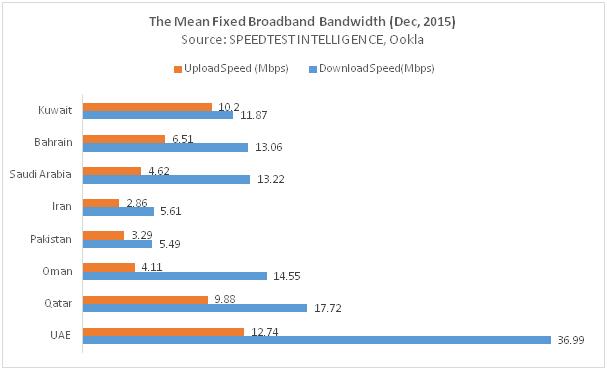
On average, GCC countries offer better bandwidth speed than Pakistan and Iran, with the UAE, Qatar, Oman and Saudi Arabia leading the way in both speed and quality of service. Qatar and the UAE particularly have almost completed their fiber to the X (FTTX) network construction, a broadband network architecture using optical fiber cables for high speed connectivity.
While Saudi Arabia continues with its implementation of the Kingdom's fiber network, Pakistan and Iran are still lagging in FTTX deployment and fixed-line internet usage is based older DSL-based networks, resulting in much lower internet speeds.
The significance of bandwidth speed becomes increasingly apparent when video comes into play. From streaming of entertainment content to live video conferencing between colleagues in different countries, video places significant demand on any broadband network. Now with HD video becoming the norm, broadband networks must now offer at least 8Mbps download speed to prevent degradation of quality and the overall user experience. Such outcomes can dramatically impact consumers' perception in the quality of experience, thus limiting the impact of these innovative internet based solutions.
On the flipside, upload speeds dramatically impact the quality of services that depend heavily on the ability of data packet to travel back and forth between one PC or device and another, such as online gaming, and for companies that are required to share large files, such as creative agencies.
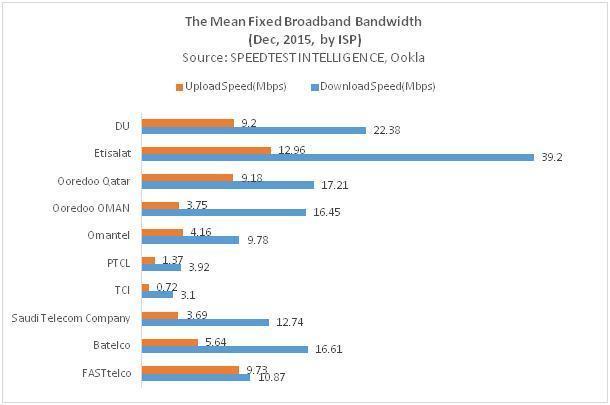
To measure the capacity of both, a mean upload/download rating is assigned as in the charts below showing the mean score by country and by operator respectively:
Impact of Latency
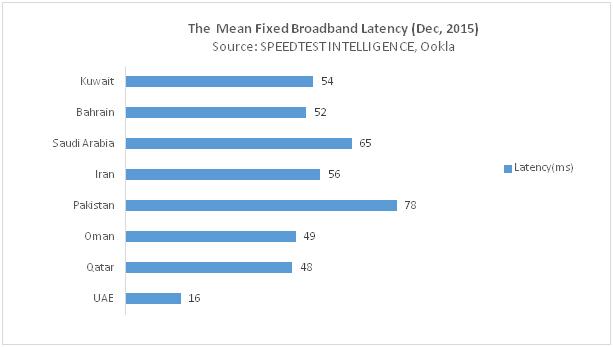
Latency, commonly known as 'lag', is expressed in terms of milliseconds (ms) and is the time it takes for a packet of data to travel from one designated point to another within the network, such as PC to PC or PC to server. Latency is a major performance benchmark and impacts overall user experience. Latency is defined as the time a packet of data makes a round-trip from a device to the closest server used to ping that packet. The lower the time it takes for the packet to come back, the better the user consumer experience is.
Today's broadband users expect an almost instantaneous response from their service providers, particularly for streaming content and online gaming where latency interferes heavily.
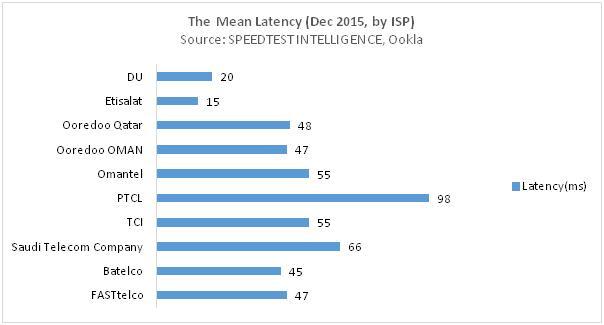
The mean latency in UAE was found to be the lowest among regional providers, thanks mainly to the UAE's advanced FTTX network, with KSA appearing to have the highest latency within the GCC as in the charts below:
National broadband strategy impact on economy
In the wake of the digital revolution, governments have adopted national broadband strategies as a critical component to ensuring their citizens are not left behind. The onset of ICT-driven solutions offers previously unimaginable economies of scale and gives governments a key role to play within the global political and economic landscape, should they play their digital strategy cards right.
Information technology currently has four major trends affecting the region:
- First - the digital standardization of acquisition and processing
- Second - high speed yet low cost information processing and transmission
- Third - collection, observation, measurement and analyzation of large scale big data
- Fourth - the deep convergence of information technology into each of the areas of society and economic sectors
This means that the investment and development of high speed broadband networks will provide greater economic opportunities to each regional country, increase civic engagement and deliver on the promise of better access to services such as healthcare and education. Moreover, it will fuel the development of a smarter power grid and with a highly interactive and responsive public safety network. A better infrastructure with broader access to improved broadband will enable innovation, including the expansion and adoption of cloud computing, more productive telecommuting, online learning, telemedicine and more. A better connected system will also allow for increased efficiency, reducing environmental emissions significantly and improving productivity.
The World Economic Forum formally recognized ICT's role in the global economic recovery strategy in 2009 stating that new technologies will not only continue to fuel growth, but also enable a digital revolution capable of uplifting economies untouched by the industrial revolution. The rise of the digital revolution has meant that governments, both regionally and around the world, have become increasingly focused on investing into their ICT infrastructure while providing stronger broadband connections to support innovation. With that being said, ultra-broadband will not only provide a better experience to end consumers, but also significantly impact national economies, allowing them to increase growth and sustainability.









